Microwave Ablation Breast Lump Treatment
Microwave Ablation Breast Lump Treatment
Microwave Ablation Breast Lump Treatment
Microwave Ablation Breast Lump Treatment
Microwave ablation induces Th1-type immune response with activation of ICOS pathway in early-stage breast cancer.
Is Microwave Ablation Breast Lump treatment Expensive?
Abstract
Background Despite great advances in the treatment of breast cancer, innovative approaches are still needed to reduce metastasis. As a minimally invasive local therapy (not standard therapy for breast cancer), microwave ablation (MWA) has been attempted to treat breast cancer, but the local effect and immune response induced by MWA have seldom been reported.
Methods The clinical study was performed to determine the complete ablation rate of MWA for early-stage breast cancer. Secondary endpoints included safety and antitumor immune response. 35 subjects from this clinical study were enrolled in the current report, and the local effect was determined by pathological examinations or follow-up. To investigate MWA-induced immune response, patients treated with surgery (n=13) were enrolled as control, and blood samples were collected before and after MWA or surgery. The immune cell populations, serum cytokines, secretory immune checkpoint molecules, and T-cell receptor sequencing were analyzed.
Results Of 35 enrolled patients, 32 (91.4%) showed complete ablation. Compared with surgery, MWA induced significantly increased levels of inducible co-stimulator (ICOS)+ activated CD4+ T cells and serum interferon gamma, indicating a shift in the Th1/Th2 balance toward Th1. The activated ICOS pathway was involved in the MWA-induced adaptive immune response. T-cell receptor sequencing revealed MWA of primary tumor activated T lymphocytes expansion and recognized some cancer-specific antigens. Moreover, CD4+ effector memory T-cell response was induced by MWA, and the immune response still existed after surgical resection of the ablated tumor.
Conclusions MWA may not only be a promising local therapy but also a trigger of antitumor immunity for breast cancer, opening new avenues for the treatment of breast cancer. Combinatorial strategy using additional agents which boost MWA-induced immune response could be considered as potential treatment for clinical study for early breast cancer therapy.
Data availability statement
All data relevant to the study are included in the article or uploaded as supplementary information. All data needed to evaluate the conclusions in this paper are present in the paper and/or the supplementary information file. Additional data related to this paper may be requested from the authors.
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/
This is an open access article distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited, appropriate credit is given, any changes made indicated, and the use is non-commercial. See http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/.
What is Microwave Ablation Breast Lump Treatment?
Microwave ablation (MWA) therapy has been widely used in treating liver tumors, but it has been rarely reported in spinal metastases treatment. Given the long survival period of breast cancer patients and the superficial thoracic anatomic position, treating thoracic metastases with MWA is beneficial and easy. Therefore, this study was designed to assess the feasibility and outcome of MWA performed for patients with breast cancer thoracic metastases. It aimed to assess the safety and short-term efficacy of MWA in patients with breast cancer thoracic metastases.
How Microwave Ablation Breast Lump Helps?
Breast tumor is the most commonly diagnosed tumor in women.
Percutaneous ablation is a minimally invasive method for the treatment of breast guided by using ultrasound (US) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which has intrigued extensive attention as a possible first-line treatment to substitute for breast surgery procedures, such as lumpectomy.
Imaging technologies are crucial to localize the target area and to assess the treatment effect during and after ablation treatment. US is most valuable in providing the location of the electrode within the lesion and in real-time monitoring the ablation.

In recent years, several ablation techniques, including radiofrequency ablation (RFA), laser ablation, cryoablation and microwave ablation (MWA) have been evaluated in clinical trials .
Compared with others ablation techniques, MWA is a promising technique because it can preferentially heat and damage high-water-content breast tumors, whereas the lesser degrees of heating lower-water-content fatty and glandular tissues.
Microwave ablation was a safe and efficient method in the treatment of the benign breast tumors.
Why choose Maven Medical Center.
- First Laser Center in both Telangana & Andhra Pradesh
- First time in INDIA,Maven Medical Center Introduced Microwave Ablation
- First NABH Pre accreted Daycare Laser Center in INDIA
- More than 15 years of experienced doctors
- 98% Success rate
Best Microwave Ablation Breast Lump Treatment In Kuala Lumpur, Selangor, Pennang Malaysia!
Microwave ablation (MWA) is a minimally-invasive treatment for cancer. MWA uses ultrasound, computed tomography (CT), or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to guide placement of a needle-like probe into a tumor. MWA uses microwaves to heat and destroy the tumor. Doctors use MWA for the same indications as RFA.
WSM MEDIC provides best Microwave Ablation Breast Lump Treatment in Malaysia.
Microwave Ablation Breast Lump Treatment in Malaysia.
Laser ablation therapy is a less invasive alternative to traditional breast cancer operations like lumpectomies. Rather than surgically removing the tumor and a small amount of surrounding tissue, this procedure uses targeted lasers to precisely destroy small tumors.
What is breast cancer?
Breast cancer occurs when a group of cells in the lobules (milk producing glands) or the ducts become abnormal and divide uncontrollably, damaging healthy tissues of the breast. It can be a benign (non-cancerous) tumour, or malignant (cancerous) breast cancer.
A benign breast tumour is abnormal growths, but they do not spread outside of the breast. They are not life threatening, but some types of benign breast lumps can increase a woman's risk of getting breast cancer. Whilst malignant breast cancer occurs when the cells divide uncontrollably and begin to invade the surrounding breast tissue and may eventually spread via blood vessels and lymphatic channels to the lymph nodes, lungs, bones, brain and liver.
Facts:
Did you know that one in every 19 women in Malaysia are at risk of developing breast cancer? According to the National Cancer Registry, it is the most common form of cancer affecting women in Malaysia. Majority of time breast lumps are biopsy-proven benign, however, about 20% of the time the breast lumps are cancerous.
Don’t worry! The chances of surviving through this disease is increasing over the years as a result of earlier detection and cutting-edge technology for the treatment.
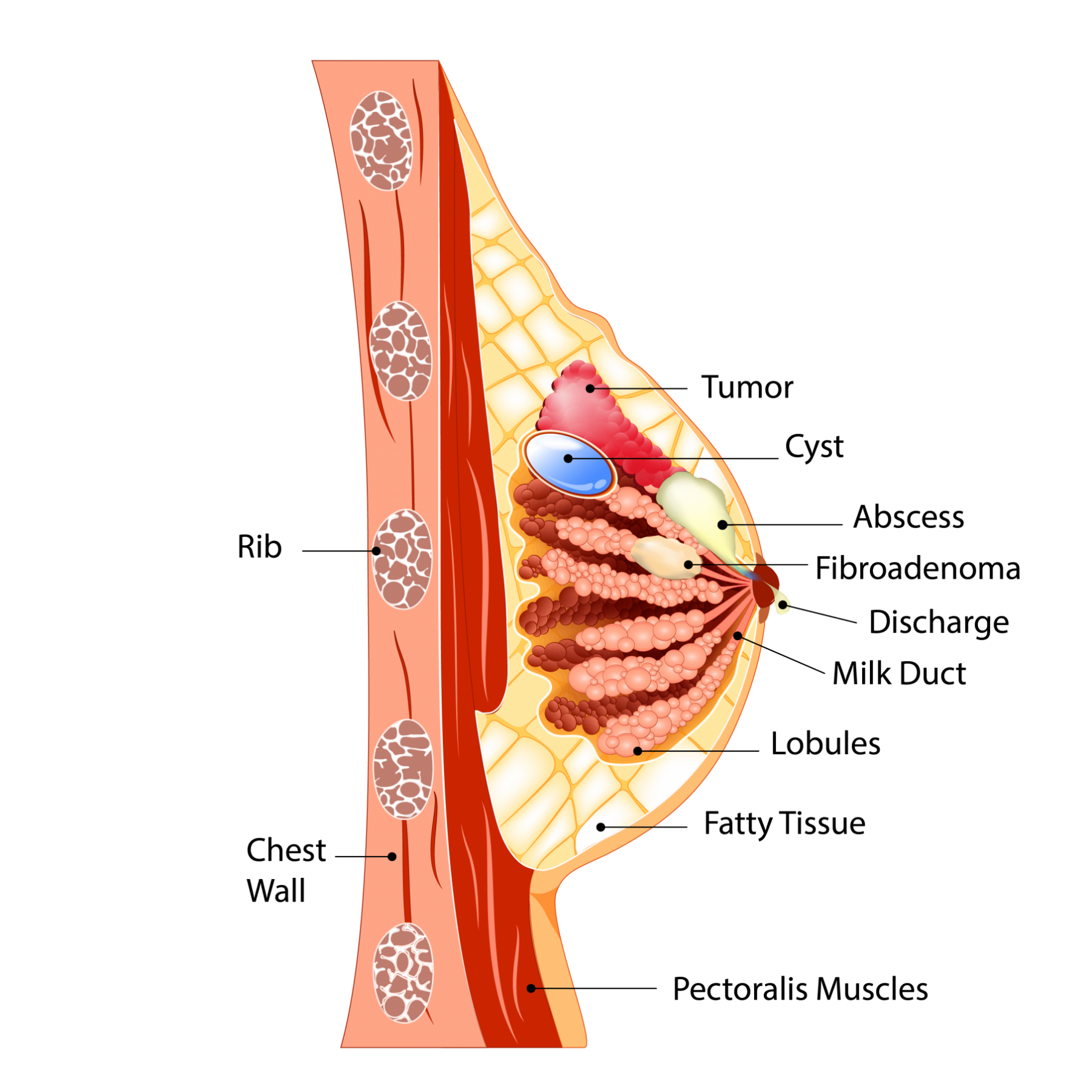
Benign Breast Lumps: Three Categories
While a benign breast lump is not currently linked to cancer, it may increase your risk of developing breast cancer in the future. Breast diseases are classified by medical specialists based on their chance of developing breast cancer.
A) No increase in risk: Also called non-proliferative breast lumps or lesions, they are usually not related with a later risk of developing into breast cancer. Common examples of such conditions include fibroadenomas and cysts.

Breast fibroadenomas are the most common form of non-cancerous solid breast lumps that consist of glandular and connective tissue. They can occur at any age, but women between 20s and 30s get them most often.
They are often painless and found near to the surface of the breast. You may feel round and firm lumps which can move freely beneath the skin when you push on them.
Breast cyst is a benign fluid-filled sac in the breast tissue that usually affect both breasts. One may have one or many, and they often vary in size. They are very common and can occur at any age. However, they are often most noticeable in women ages 40s who are in perimenopause (the period of time before menopause when a woman stops having periods). It is less likely to notice on postmenopausal women due to lack of monthly changes in hormones.
Breast cysts can be located anywhere in the breast – near the surface or deep inside. You may feel smooth and soft, like a water balloon when you press on it. Its tenderness and size often change with your menstrual cycle. They can also be painful or tender, especially just before your menstrual period begins.
For an accurate diagnosis, fine needle aspiration may be needed. Simple cysts are less likely linked to breast cancer.
B) A slight increase in risk: With such conditions, the risk of cancer is usually very low. Doctors must occasionally keep a careful eye on them to ensure that the cells do not continue to divide. Fat necrosis and duct ectasia are the examples of such conditions.

Fat necrosis is a type of breast lump consists of dead or scar breast tissue that’s been damaged by surgery or trauma. They are generally round, firm, hard and painless. A fat necrosis could cause breast discharge, and dimpling of the nipple and skin.
For an accurate diagnosis, doctor will perform a biopsy test on you as it can mimic cancer on the imaging tests.
Duct Ectasia is one type of benign breast tumour occurs when the milk ducts become clogged and swollen. It is often appeared as a small lump just under your nipple, causing a greyish discharge or nipple to be retracted inward. This benign condition is most commonly seen on women around the age of menopause.
C) A moderate increase in risk: Also known as “pre-cancerous breast lumps”, a condition in which cells are dividing excessively and may transform into cancer cells in the future. Common examples of such condition are intraductal papillomas and hyperplasia.

Intraductal papillomas are a type of pre-cancerous breast lumps which are small in size and begin in the lining of mammary duct near the nipple. They usually affect women who are under 30s to 50s, and often cause bleeding from the nipple.
Hyperplasia of breast occurs when the cells that line the ducts or lobules of the breast grow out of control. It is very difficult to differentiate as they may still look normal in appearance though the cells are more numerous than they should be. There are two conditions of hyperplasia – usual hyperplasia and atypical hyperplasia. Usual hyperplasia doesn’t increase the risk of breast cancer, whereas atypical hyperplasia will be advised to remove as this condition may cause you more prone to breast cancer
What you should know about risk factors of breast cancer
Factors that may put you at risk of breast cancer include:
Sign and Symptoms
Knowing how your breasts normally look and feel is an important part of breast health. You should see a doctor if you notice any change in your breasts and observe the signs and symptoms as below:
While the following symptoms could also be shared by other illness, early-stage cancer doesn’t cause pain and you should see your doctor for a full diagnosis and early treatment.

How does a breast lump feel like?
A benign breast lump will usually be smooth and spongy, and will move when you push on it, whereas a cancerous breast lump will be harder and immobile when you pushed.
Breast lumps can vary in size, rate of growth and symptoms. It is advisable to see a doctor when you first notice one as it is difficult to distinguish the cause of a lump based on breast self-examination.
Diagnosis
Is it possible to prevent breast cancer?
The best way to prevent breast cancer is for you to be breast aware. It is crucially important to observe and understand how your breast look and feel like under normal circumstances, so that you are able to seek early medical advice if there are any changes in either breast.
a) Breast Self-Examination
Note:
- Every month, women should perform a breast self-exam. About 3 to 5 days after their period start, women who are still menstruating (have a regular period) should undertake a breast self-exam consistently on the same day of every month.
- Women who have stopped menstruation or whose periods are exceedingly irregular can choose a day each month.
Set a reminder on your calendar, be sure to perform breast self-examination monthly.
Seek for medical advice if you notice any changes on your breast. Doctor will perform either or all of the following examinations for better diagnosis.
b) Clinical Breast Examination (CBE)

Clinical Breast Examination (CBE) usually conducted by a doctor to spot for changes such as size, shape, texture and mobility of the lump. Benign lumps are usually soft, smooth, round and movable.
c) Ultrasound

Ultrasound is able to detect whether a lump is solid or filled with fluid. Fluid-filled sacs like cysts are non-cancerous, but a solid mass may be cancerous.
d) Biopsy

Biopsy may be used along with ultrasound, which is a kind of test that involve removing fluid or tissue from your breast for further diagnosis.
e) Mammogram
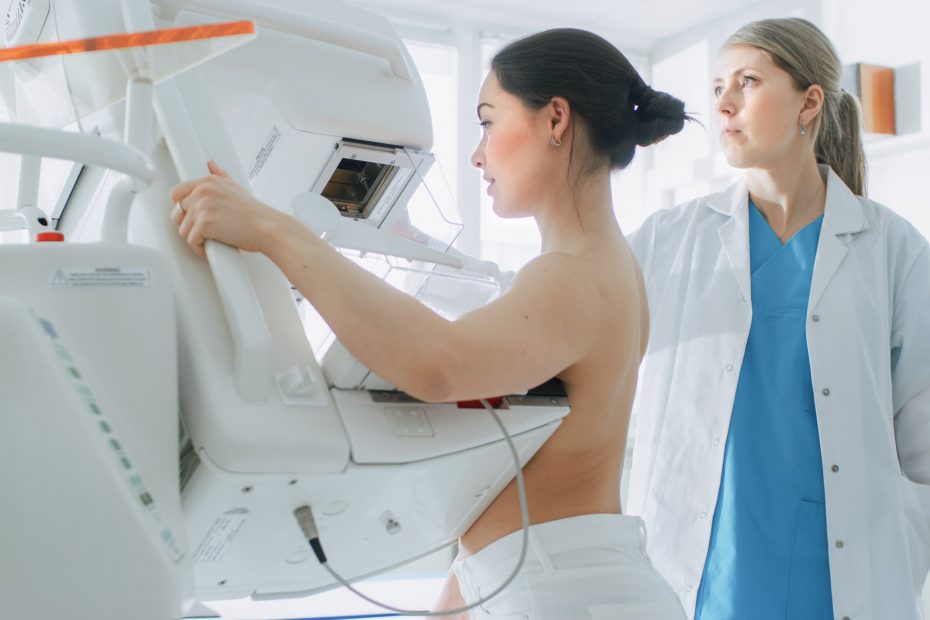
Mammograms is able to detect breast tumour when it is small and even before symptoms can be observed. It may be recommended by the doctor for further diagnosis on the changes in breast tissue.
What are the types of surgery available for benign breast tumour?
Mastectomy
A mastectomy is surgery to remove a breast. Sometimes other tissues near the breast, such as lymph nodes, are also removed. This surgery is most often used to treat breast cancer. A conventional treatment called total mastectomy which is an invasive surgery, removing the entire breast (either one or both breasts) and usually some underarm lymph nodes. It may require a stay of 5 to 10 days in the hospital. It is often found to be psychologically difficult to accept as the whole breast will be removed, facing cosmetic issue. It may also pose increase risk and difficult in re-operation for recurrent lesions.


Lumpectomy
Lumpectomy is a type of breast conserving surgery which involves surgical removal of the tumour and some of the surrounding tissue while preserving the breast structure. Though this type of surgery is less invasive, yet there may be a scar leaft behind and may cause distortion of breast (change in breast shape). This procedure may also cause damage to the milk duct, affecting breastfeeding in the future.
Vacuum Assisted Biopsy (VAB)
VAB is a type of minimally invasive surgery as compared with the traditional surgical treatment. 1) In this procedure, an automated cutting mechanism cuts the breast tissue repeatedly in several directions, 2) breast tissue will be removed or sucked out through a hollow needle device with a vacuum suction. Doctor will move up and down repeatedly in several directions to cut and remove the abnormal breast tissue until the whole area is covered.
In short, Vacuum Assisted Biopsy Surgery treats benign breast tumour by removing or sucking out breast tissue through a vacuum device. After the procedure, doctor may compress on the breast to stop the bleeding and reduce the risk of hematoma. Skin dimpling may occur.

Thermal Ablation For The Treatment Of Benign Breast Tumour
The Latest Thermal Ablation Treatment
Microwave Ablation
Is a minimally invasive thermal ablation treatment available for benign breast tumours without cutting open and removing any breast tissue.

Did you know?
The same Microwave Ablation (MWA) Technology has been available in Malaysia since year 2012, widely used by Interventional Radiologists to treat solid cancerous tumours in liver, lung, kidney, adrenal, spleen, bone and others as a Minimally Invasive Cancer Therapy.
Why Microwave Ablation?
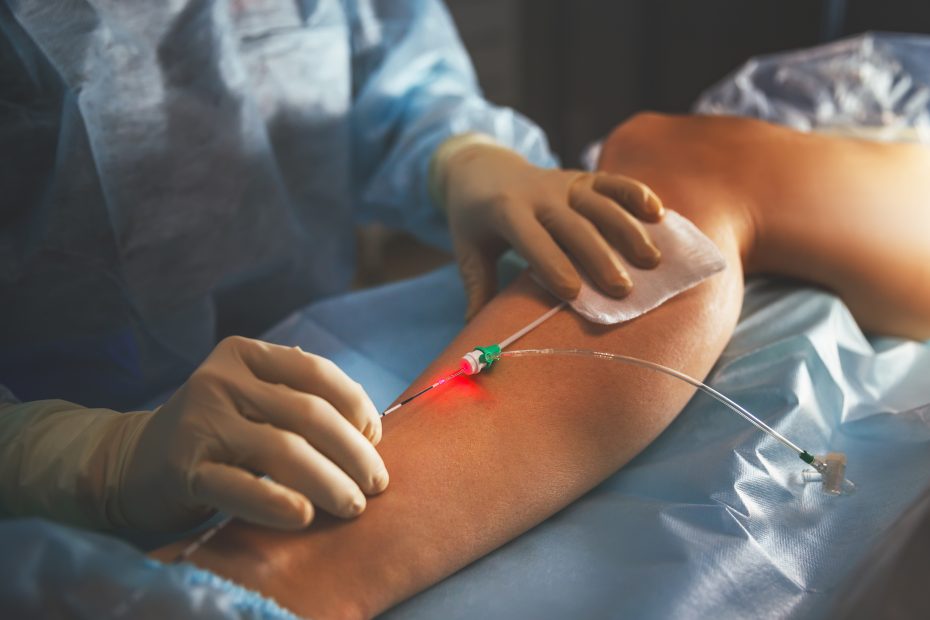
This procedure is precise and safe. Ultrasound is utilized during the procedure to clearly locate the tumour and monitor the needle placement and ablation. During the procedure, doctor will insert a microwave antenna (needle) as small as 1.6mm in diameter through the skin under real-time image guided by ultrasound into the tumour, once it is in position, microwave energy will be activated to kill the tumour cells. A fine needle prick is left which heals quickly after the procedure.
MWA procedure is a quick Day-Care Procedure that generally takes about 30 minutes, depending on the size of tumour. A tumour size of 3.0cm in diameter can be ablated in 5 minutes. Thanks to the advancement in Microwave Technology as it is not limited by the types of tissue for conductivity, MWA is able to achieve larger homogenous ablation zone in a shorter time.
How does Microwave Ablation works?
MWA uses electromagnetic wave to produce tissue heating effect. The oscillation of polar molecules produces frictional heating, ultimately generating tissue coagulation necrosis within the tumour. It destroys and eradicate non-cancerous breast tumors (lumps) by ablating them with thermal ablation.
Mechanism of Microwave Thermal Ablation generates a series of biochemical changes, such as tumour cell dehydration, intracellular protein denaturation and coagulation that brings the synthesis of tumour cell’s deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and protein to a halt. It also destroys the blood supply of the lesion, which results in necrosis of tumour cells. The treated tumour will be absorbed by body over time, no tissue removal is required.
What are the advantages of Microwave Ablation?
MWA is a minimally-invasive treatment, with benefits as follows:
Almost painless, without cutting or stitching
Nearly scarless or tiny wound size of 1.6mm
The breast maintains its volume and shape as no breast tissue removal
Day-care or only one-night stay in hospital
Fast procedure time (30 – 60 minutes)
Recovery is quick
Local anaesthesia (LA) is possible
What to expect after MWA Breast Treatment?
- After the procedure, some swelling may occur. Doctor may prescribe cold compression to be applied on the treated area with ice pack to reduce the swelling.
- Tumour cells are destroyed during the procedure. It is normal that patient can still feel a lump in the beginning, but this will become softer gradually shrink and absorbed by the body. This process can be monitored by ultrasound during follow up visits.
- Wear a bra 24 hours a day
- Apply a waterproof plaster for at least 72 hours
- No exercise or heavy lifting for a few days
- Bruising is slight, if any, and will go away on its own within seven days
- Return for a check-up with the doctor after one week
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How is the Microwave Ablation Treatment for Breast Tumour (Lump) Different from Traditional Open Surgery?
Microwave Ablation treats breast tumour by inserting a tiny antenna (needle) as small as 1.6mm in size, percutaneously (through skin) into the targeted area with real-time imaging guidance by ultrasound, to ablate the tumour. A small water-proof plaster is applied to close the needle nick. Whereas traditional open surgery is performed using sharp dissection with a scalpel or scissor technique depending on the severity of the condition, either whole or part of breast will be cut out and removed. Stiches will be applied to close the skin.
MWA maintains the breast volume and shape as cutting or removal of breast tissue, and stiches are not necessary. MWA is a minimally invasive option for the treatment of breast lump.
2. How long is the MWA Procedure?
The entire procedure generally takes about 30 to 60 minutes including preparation, ultrasound scanning before procedure, microwave ablation, and ultrasound scanning after procedure. The Microwave Ablation alone takes only about 5 minutes.
3. How long is the recovery period or when can I back to normal activities after Microwave Ablation?
The MWA Treatment is a Day-Care Procedure whereby patient can go home on the same day, or stay in the hospital for only one night. You may resume back to normal daily activities such as eat, drink, move around immediately right after Microwave Ablation. This treatment does not require long bed rest for recovery.
From the feedback of patients who have gone through MWA procedure, most of them felt close to normal even on the same day, and were able to do simple daily activities. However, patients are advised to rest for three to seven days to recuperate. This will help the patient to get comfortable with the body changes and regain her confidence.
4. Will there be any complications?
From the feedback of patients who have gone through MWA procedure, no major complications such as skin burn, bruises, haematoma, infections or other adverse effects were observed.
After the procedure, a palpable lump (dead tissue in the treated are) and mild breast swelling can be expected, which is normal. The swelling is usually not painful or causing any discomfort as the body will re-absorbs it over time. The sensation of a palpable lump will become softer and smaller in size gradually, may take several months (up to one year) to disappear completely depending on the treated tumour size.
5. Can I still breastfeed after Microwave Ablation?
Yes, Microwave Ablation will not affect or cause damage to the milk duct. As a result, it will not affect the breastfeeding in the future.
6. Do I have to get smaller-sized bras to wear while healing? Will my breast change its shape, or will the volume become smaller after treatment?
No, you do not require smaller-sized bras to wear during healing, as there is no loss of breast volume or change in breast shape after MWA procedure. MWA is a type of percutaneous method of ablation, in which needles are inserted through the skin. No incision or removal of breast tissue is required for this procedure.
The appearance of your breast is virtually the same as before.
7. Will there be any scar on my breast after Microwave Ablation Treatment?
No, only a small nick on the skin is made to insert a fine needle as small as 1.6mm in diameter into the tumour during MWA procedure. A small water-proof plaster is applied to close the needle hole. There is hardly any visible scar as it does not require any cutting, tissue removal, or stitching.
8. Do I require any breast implant after the treatment?
No, your breast will remain intact after Microwave Ablation Treatment as there is no cutting and tissue removal needed. Hence, you do not need any breast implant afterward 😊
9. Is sensation in the breast affected by Microwave Ablation?
Patients reported that MWA did not cause any loss of sensation or feeling in the treated breast.
10. Can Microwave Ablation be done if there is more than one tumour in the breast?
Yes, even if the tumours are located in different locations of breast.